When it comes to creating structures or products using aluminum extrusions, choosing the right joining method is crucial. Aluminum extrusion is a versatile process that allows for the creation of complex shapes and designs, but how these pieces are connected together can significantly impact the strength, appearance, and functionality of the final product. In this blog post, we will explore various aluminum extrusion joining methods commonly used in the industry.
Screw Ports
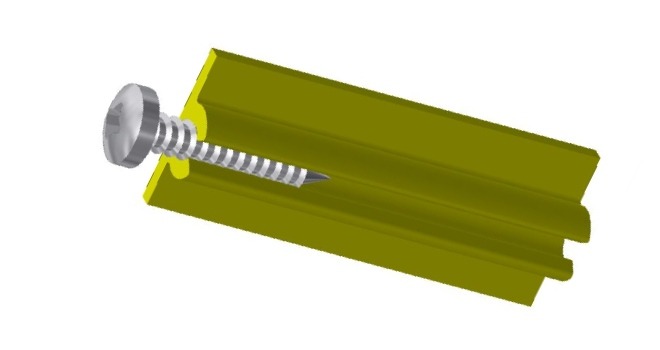
Screw ports serve as foundational elements within the framework of aluminum extrusion design, offering a versatile solution for securing components. Designed to be compatible with both self-tapping and machine screws, these ports provide a reliable and sturdy connection that can be conveniently disassembled when required. The key to their effectiveness lies in ensuring there is ample clearance to accommodate the screw head, thereby facilitating a secure and stable fit within the port.
By incorporating screw ports into extrusion designs, engineers and designers benefit from a practical and efficient method of joining aluminum components. This feature not only enhances the ease of assembly but also simplifies maintenance tasks, allowing for seamless disassembly for repairs or modifications. Attention to detail in aligning and fastening screws within the ports is crucial to uphold the strength and integrity of the overall structure.
Differences Between Self-tapping and Machine Screws
In the realm of aluminum extrusion joining, self-tapping screws and machine screws play distinct roles:
Self-Tapping Screws:
- Function: Self-tapping screws feature notched tips that enable them to create threads as they are driven into materials, eliminating the need for pre-drilled holes.
- Application: Ideal for materials like aluminum and wood, self-tapping screws offer quick and efficient assembly without requiring pre-drilling.
- Advantages: They provide rapid assembly and a strong grip due to the threads they form directly in the material.
Machine Screws:
- Function: Machine screws are used with pre-drilled holes and nuts or threaded inserts to secure components together.
- Application: Commonly employed in machinery, appliances, and electronics, machine screws offer precise and secure fastening.
- Advantages: They deliver a high level of precision and strength, allowing for controlled tightening and robust connections when paired with nuts or threaded inserts.
Flat Joints

Flat joint represents a distinctive category among aluminum extrusion joining methods, differing from others on this list by their direct alignment without specialized mating surfaces. These joints, whether configured as butt joints, lap joints, tee joints, or other arrangements, rely on external support mechanisms like welding or fasteners for structural integrity, as opposed to inherent geometric features.
The versatility of flat joint allows for various configurations, each requiring additional reinforcement to maintain cohesion. Common examples within this method include tee joints, butt joints, edge joints, and lap joints, where the simplicity of alignment necessitates supplementary support for a secure and durable connection.
Features Of Flat Joints
Within aluminum extrusion projects, flat joint encompass various types, each with distinct features shaping their utility:
Tee Joints
Tee joints in aluminum extrusion entail the perpendicular alignment of two extrusions, forming a T-shaped connection. This type offers structural support for applications necessitating a right-angle attachment, typically requiring additional reinforcement through welding or fasteners.
Lap Joints
Lap joints feature one extrusion overlapping another, establishing a layered connection that increases surface area for bonding. This configuration requires fasteners or adhesives to secure the overlapping sections, offering versatility in applications requiring a robust, overlapping connection.
Edge Joints
In edge joints, the edges of two extrusions are brought into contact, creating a flush connection. Additional fasteners or adhesives are commonly employed to maintain alignment and stability in this type of joint.
Butt Joints
Butt joints involve aligning the ends of two extrusions flush with each other. This straightforward method ensures a seamless end-to-end connection, often relying on welding or fastening solutions for secure bonding.
Snap Fit

A convenient joining method in aluminum extrusion is the snap fit, offering a swift and uncomplicated way to secure two extrusions. This technique can serve as a decorative element, concealing unsightly screw heads and enhancing the overall aesthetic. Moreover, snap fits eliminate the need for additional fixings, simplifying the recycling process.
The mechanism involves lead-in barbs that enable the upper extrusion to slide smoothly over the lower one, engaging with a satisfying snap due to the inherent flexibility of aluminum. It’s crucial to note that a barb lacking a reverse chamfer may result in a permanent snap-fit, emphasizing the importance of precision in the design and execution of snap-fit connections.
Design Considerations for Effective Snap Fits in Aluminum Extrusions
When creating snap fits in aluminum extrusions, several key design considerations are essential to ensure the effectiveness and reliability of the connection:
Material Selection: Choose aluminum alloys that offer the necessary strength and flexibility for snap-fit applications. Consider factors such as elasticity and durability to withstand repeated snapping without deformation.
Geometry: Design precise lead-in features like barbs or clips on the extrusions to facilitate easy alignment and engagement during assembly. Ensure that the geometry allows for a secure snap without compromising the structural integrity of the extrusions.
Tolerances: Maintain tight tolerances to guarantee a snug fit between mating components. Proper tolerancing helps prevent excessive play or interference, ensuring a secure connection while allowing for smooth assembly.
Chamfers and Radii: Incorporate appropriate chamfers, fillets, or radii at critical points to prevent stress concentrations and facilitate smooth engagement and disengagement of the snap fit.
Interlocking Joints

Interlocking joints are a simple yet effective type of geometry-based connection in aluminum extrusions. Unlike joints that require fasteners or adhesives, interlocking joints are created by rotating two components into place. This aluminum extrusion joining method offers a sturdy connection that can be quickly disassembled by counter-rotating the components out of position.
To enhance the stability of interlocking joints and prevent accidental disassembly, additional elements can be introduced. These elements function similarly to key-locked joints, adding an extra layer of security to the connection.
Interlocking Joints Applications
Interlocking joints in aluminum extrusions find various applications across industries due to their simplicity and effectiveness. Some common uses include:
Furniture: Interlocking joints are often employed in the assembly of aluminum extrusion furniture frames, providing a sturdy and secure connection without the need for additional fasteners.
Automotive Components: Aluminum extrusion interlocking joints are integrated into automotive applications for assembling various components, such as roof racks, cargo systems, and interior trim pieces.
Equipment Frames: Industrial equipment frames benefit from the simplicity and reliability of interlocking joints in aluminum extrusions, offering a cost-effective solution for constructing robust and customizable frames.